Virtual Power Plants are no longer a purely theoretical concept; they are rapidly becoming a core trend in modern energy management. By seamlessly integrating digital technology with renewable energy, VPPs open up a future where power systems operate in a more flexible, intelligent, and sustainable manner.
Instead of relying solely on centralized conventional power plants, the Virtual Power Plant model enables the effective connection and coordination of multiple distributed renewable energy sources. TMT Energy delivers Virtual Power Plant solutions that leverage solar power, wind energy, hydropower, biomass, and other renewable resources to create a stable, optimized, and environmentally friendly power supply system.
What is a Virtual Power Plant?
A Virtual Power Plant (VPP) is a system that utilizes digital technologies, control software, and intelligent information systems to connect, monitor, and coordinate multiple distributed energy resources. Although these resources are geographically dispersed, they can be operated synchronously as a single unified power plant.
In traditional models, power systems follow a centralized structure, where large power plants generate electricity and transmit it to end users. However, the rapid growth of distributed renewable energy—such as rooftop solar systems and small-scale wind power—has introduced new challenges in managing, balancing, and stabilizing the power grid.
The Virtual Power Plant was developed to address these challenges by:
-
Optimizing the utilization of renewable energy resources
-
Enhancing real-time monitoring and system coordination
-
Reducing dependence on fossil fuel-based power generation
-
Contributing to the development of a more flexible, intelligent, and sustainable energy system
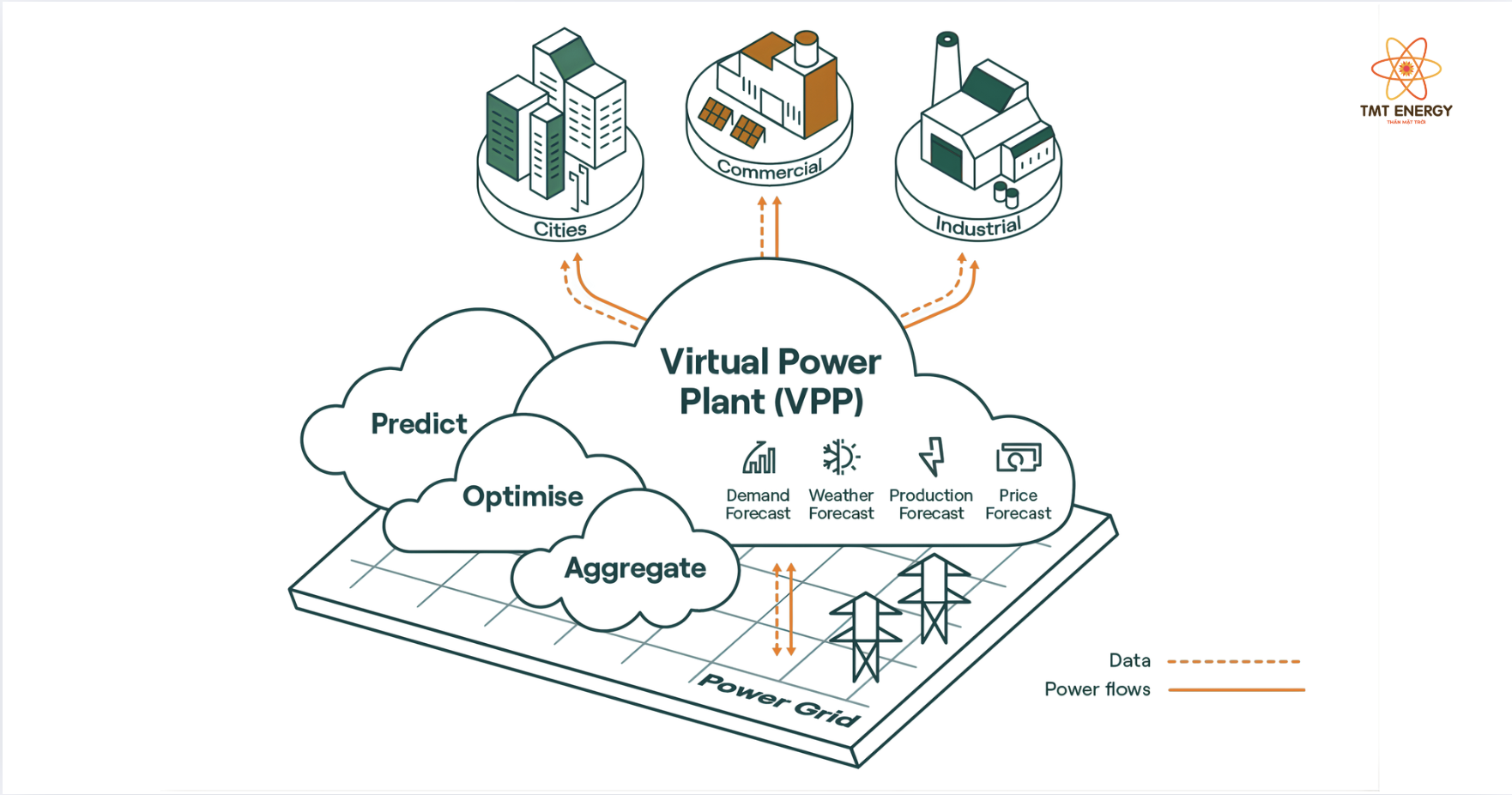
Benefits of Virtual Power Plants
Virtual Power Plants (VPPs) are becoming a key solution in the global energy transition, enhancing power system efficiency while promoting sustainable development. Beyond being a management tool, VPPs deliver tangible value to businesses, grid operators, and the environment.
Optimized Energy Utilization
Virtual Power Plants enable the intelligent connection and coordination of distributed energy resources, maximizing the potential of renewable energy. Through advanced data analytics and demand-based control, VPPs reduce energy waste, improve operational efficiency, and optimize electricity costs.
Enhanced Grid Stability and Flexibility
With real-time monitoring and control capabilities, VPPs support load balancing, power regulation, and rapid response to fluctuations in electricity demand. This helps prevent overloads, imbalances, and power supply disruptions, while increasing the grid’s ability to adapt to variable renewable energy sources.
Reduced Emissions and Environmental Protection
By prioritizing renewable energy usage and optimizing system operations, Virtual Power Plants reduce dependence on fossil fuels, thereby lowering greenhouse gas emissions and environmental pollution. VPPs play a crucial role in helping both businesses and power systems move closer to sustainable development and a green economy.
Efficient Energy Distribution Systems
Virtual Power Plants facilitate the effective integration of distributed energy resources into existing power infrastructure. The close coordination between distributed sources and the transmission grid helps create a stable, flexible, and reliable energy distribution system capable of meeting growing electricity demand.
Improved Responsiveness and Flexible Services
Leveraging intelligent forecasting and dispatch tools, VPPs can provide a range of value-added services such as power adjustment, load balancing, and demand optimization. This enables the power system to respond quickly to supply–demand changes, ensuring energy security and long-term operational stability.
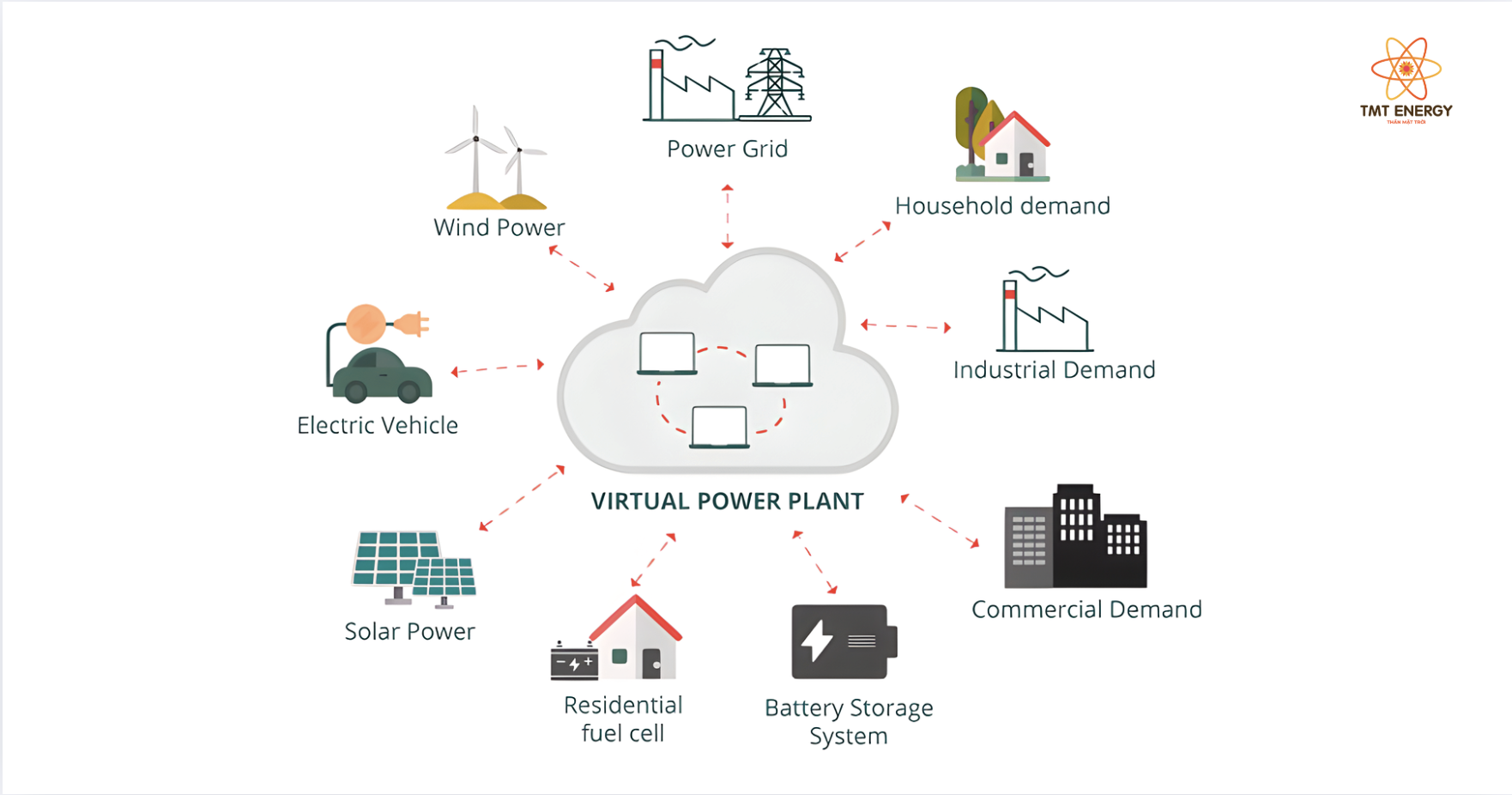
How Virtual Power Plants Work
A Virtual Power Plant (VPP) operates by intelligently integrating and managing distributed energy resources to form an efficient, flexible, and reliable energy system.
1. Aggregation of Distributed Energy Resources
Virtual Power Plants aggregate various energy sources such as solar power systems, wind power, battery energy storage systems (BESS), electric batteries, waste-to-energy systems, and other distributed resources.
Although these resources are geographically dispersed, they are connected through the power grid and digital communication platforms, allowing them to operate collectively as a single power plant.
2. Real-Time Monitoring and Data Collection
VPPs utilize advanced monitoring technologies to continuously collect data on power output, energy production, equipment status, weather conditions, and grid performance.
This data is transmitted to a central control system, forming the foundation for analysis, optimization, and operational decision-making.
3. Energy Demand Analysis and Forecasting
The VPP control center applies analytical and forecasting algorithms to estimate short-term and long-term energy demand.
Based on real-time and historical data, the system can predict consumption patterns and proactively adjust the operation of distributed energy resources to meet demand efficiently.
4. Supply Control and Optimization
Using demand forecasts and system constraints, the Virtual Power Plant dynamically controls power output, battery charging and discharging, and load balancing across the network.
This ensures a stable energy supply, reduces stress on the grid, and improves overall system efficiency.
5. Service Provision and Market Interaction
Beyond internal management, Virtual Power Plants can deliver flexible energy services such as power regulation, load balancing, and energy forecasting to the electricity market.
By interacting with utilities, consumers, and transmission system operators, VPPs help optimize energy usage and enhance the performance of the power market.
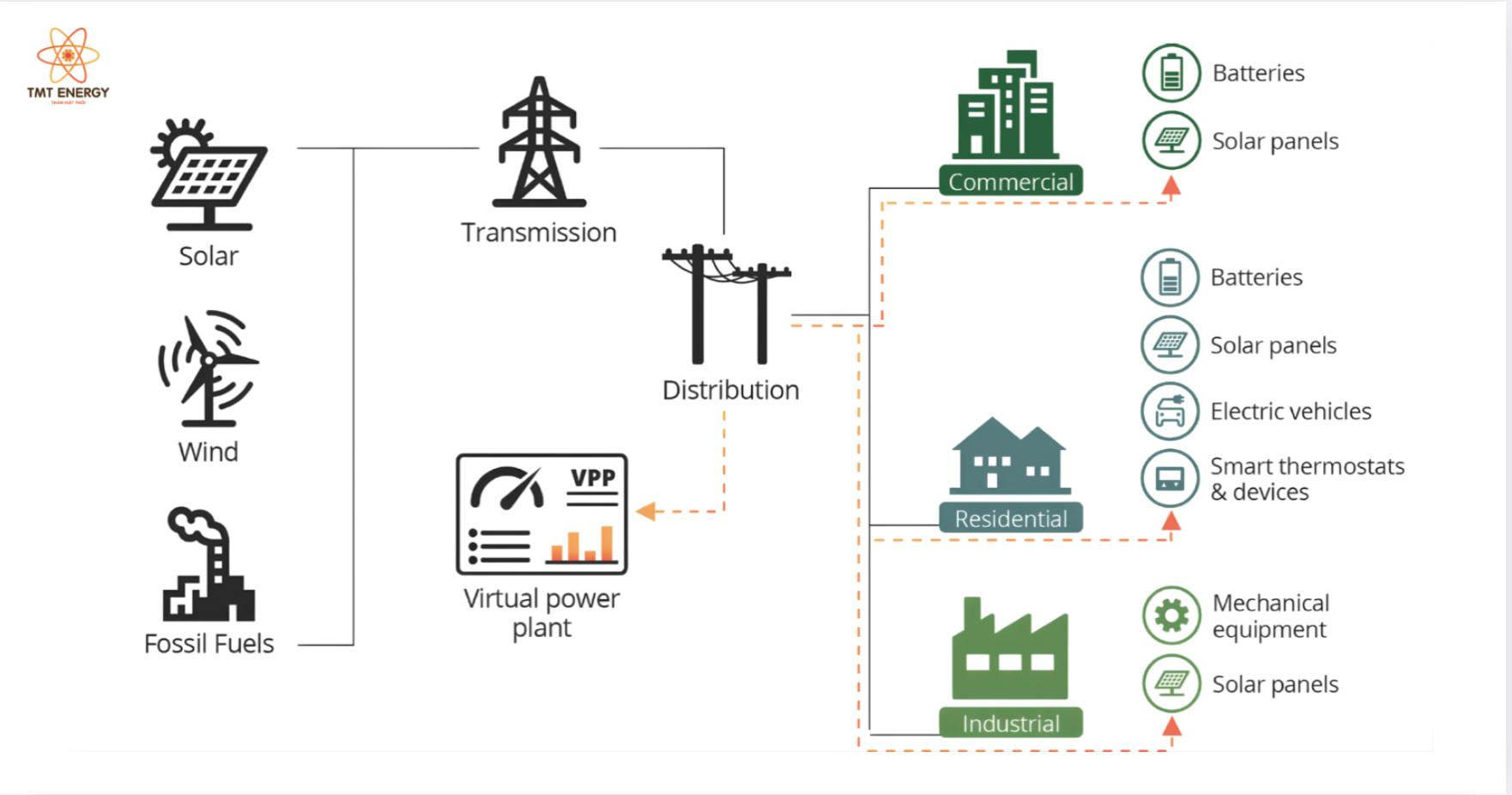
Participants in a Virtual Power Plant (VPP)
A Virtual Power Plant is a multi-stakeholder model that brings together various participants within the energy ecosystem to create shared value.
-
Energy Consumers
Consumers participate in VPPs by using smart devices, energy storage systems, and renewable energy sources. This enables cost savings, optimized energy consumption, and improved energy efficiency. -
Distributed Energy Resource Owners
Individuals and businesses that own solar, wind, or battery energy storage systems can connect to a VPP to maximize asset utilization, improve investment returns, and contribute electricity to the grid. -
Energy Service Providers
Including utilities, energy management companies, and energy aggregators. They leverage VPP platforms to deliver services such as power regulation, load balancing, and energy forecasting. -
Transmission and System Operators
These entities interact with VPPs to ensure grid stability, flexibility, and effective integration of variable renewable energy sources. -
System and Grid Operators
Responsible for monitoring, data analysis, and operational control of the Virtual Power Plant, ensuring safe, stable, and efficient system performance.

Conclusion
Virtual Power Plants are no longer merely a conceptual idea or a technological trend; they have become a practical and effective solution for building a clean, intelligent, and sustainable energy future.
Amid the accelerating global energy transition, the adoption of Virtual Power Plants enables more efficient use of renewable energy, optimized power system operations, and reduced environmental impact.
With continuously advancing technologies and scalable solutions, TMT Energy aspires to work alongside businesses and communities to promote the widespread adoption of Virtual Power Plants, contributing to the energy transition and helping shape a greener, safer, and more prosperous future for generations to come.

